''I believe that the artist must achieve creative control over the whole of his environment.''- New York Times, October 21, 1984
Herbert Bayer was intimately involved in the celebrated Bauhaus school in Germany in the 1920s and 30s: first as a student, and then as one of its directors. He emigrated to the United States in 1938. As an advocate of Bauhaus principles he produced works which expressed the needs of an industrial age, the positive collaboration between business and art, mirroring the advanced tendencies of the avant-garde.
typography by Herbert Bayer, entrance to Bauhaus image: Wikipedia
The Bauhaus was based on the principles of the 19th-century English designer William Morris and the Arts and Crafts movement that spoke of art meeting the needs of society and that no distinction should be made between fine arts and practical crafts. It was also dependent on the more forward-looking principles that modern art and architecture must be responsive to the needs and influences of the modern industrial world and that good designs must pass the test of both aesthetic standards and sound engineering. This Bauhaus style, could also be described as the absence of ornament and ostentatious facades and by a harmony between function and the artistic and technical means employed.
For over 60 years Bayer created pioneering works in painting, sculpture, environmental works, industrial design, typography, architecture, photography, and applied design. He was truly what can be referred to as “a renaissance man,” one of the few "total artists" of the twentieth century.
"Metamophosis"1936 photographic montage (image: metmuseum.org)
Marble Garden, 1955 - Aspen Meadows Hotel
In this experimental garden, Bayer introduced modernist imagery into the environment for perhaps the first time. Slabs and blocks of white marble were sourced from a nearby abandoned quarry for this thirty-eight foot square experimental garden that begins to suggests the notion that all gardens are nothing more than three dimensional sculpture. The "Grass Mound" (1955), came to inspire a whole generation of earthworks artists and initiated the ground for ecological design and restoration projects of today.
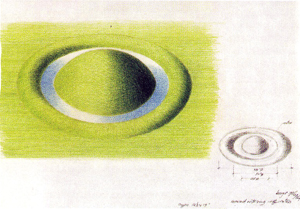
Sketches for earthworks by Bayer...
Installed in 1982, the "Earthworks" was hyped for its fusion of art and infrastructure, making the installation a powerful precedent for landscape designers, architects, engineers and artists. A series of sculpted spaces that feel both ancient and modern, the Earthworks’ pure forms of geometry -- cones, circles, lines and berms—are built into the alluvial delta at the mouth of Mill Creek Canyon. Grass and concrete, a wood bridge and steps: these are the materials at work, joined by the natural forces of Mill Creek itself. According to Landscape Architecture magazine, "the city of Kent, Washington, through its Arts Commission and Parks and Recreation Department, commissioned this project as a solution to urban stormwater runoff and its resultant soil erosion problems. The environmental artwork was a means of enlivening the plans for a proposed stormwater detention basin and creating an unusual entrance to an existing public park. The city's goals were to control flooding, to restore fish runs, and to create an aesthetically pleasing facility that would contribute to enhancing the park."
Mill Creek Canyon Earthworks 1982 (image: landscapemodeling.org)
previous images: flicker.com
Photo by John Hoge and Nancy Leahy
"Layered Landscape" 1944 gouache on paper (image: aspen journal)
In his commercial graphic design work, he was an advocate of social responsibility in design – products or services that promote positive ideas and behaviors while promoting the company. In 1941, the Container Corporation which produced 90 percent to 95 percent of its cardboard from wastepaper hired Bayer to oversee a series of posters promoting the companies ability to recycle products on a grand scale, linking corporate responsibility with the environment.
Subsequently, Bayer also oversaw another series of posters linking entitled "Great Ideas of Western Man".
"The things that will destroy America are prosperity at any price, peace at any price, safety first instead of duty first, and love of soft living and the get-rich-quick theory of life."--Theodore Roosevelt.
From the series Great Ideas of Western Man. 1959 Herbert Bayer
“In a response to the Earth Day of 1970, the Container Corporation announced a design competition for a trademark for recycling in the spirit of Bayer. The competition was won by a student at the University of Southern California presenting the symbol at the Design Conference in Aspen (Figure 7).87 Now universally known, its history goes back to the Bauhaus ideal for living in harmony with the natural world.”
-Environmental History, Peter Anker April 2007
original design for recycling (image" wikipedia)